Primary Purpose
The Activity-Based Model (ABM) is a new generation of travel
demand model. According to the 2010 RTP Guideline by California
Transportation Commission, the largest four MPOs in California
are encouraged to transition to activity-based travel demand
models for the following RTP cycle (if the model is not already
developed and validated for the current RTP cycle). This new
modeling system is designed to meet/exceed federal regulations
and state laws and requirements.
About SCAG ABM
SCAG’s ABM adopts a true activity-based approach by focusing
explicitly on activity episode generation and their
characteristics. Key model characteristics include:
-
ABM creates rich socio-economic characteristics for each
person and for each household in the SCAG region;
-
Simulates daily activities and travel patterns of all
individuals in the region, as affected by transportation
system level of services;
-
Predicts decisions “whether, when, where, for how long, with
whom and in what sequence” to participate in activities;
-
Simulates the effects of transportation and land development
investments and policies on the quality (time and cost) and
quantity (traffic volume, congestion, and vehicle miles
traveled) of travel by different modes (walk, bike, transit,
and auto); and
-
Generates performance indicators, conformity analysis, and
environmental justice analysis for the 2016 RTP/SCS. It is
being developed to be capable of analyzing the impact of
infrastructure investment, land use development, pricing
policy, active transportation, high speed rail, and travel
demand management.
Features
SCAG’s ABM incorporates a state-of-the-art approach to forecast
travel behavior in a micro-simulation framework. Major strengths
of SCAG ABM include: comprehensively characterizes the
activity-travel patterns of all household members; incorporates
spatial-temporal dependencies and constraints between and within
individuals of a household; incorporates advanced vehicle type
choice sub-model (vehicle fleet composition defined by body type,
fuel type, make/model, and vintage) for emissions analysis;
temporal and spatial resolutions; and involves a portable and
flexible object-oriented software architecture design.
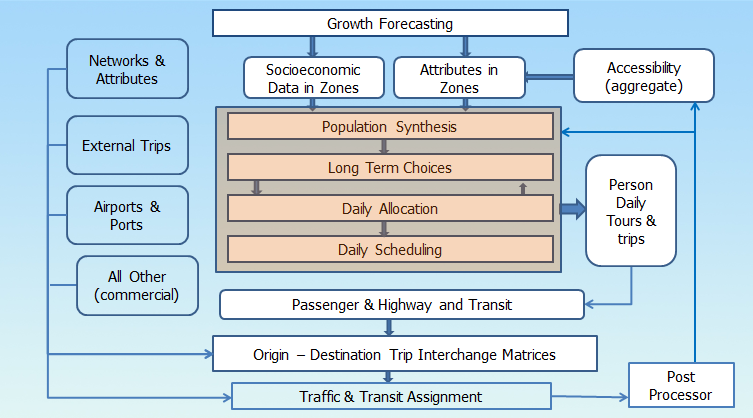
Framework
SimAGENT (Simulator of Activities, Greenhouse Emissions,
Networks, and Travel) is the base framework of SCAG’s ABM. It
includes three core modules:
-
PopGen – Generates complete synthetic population by expanding
the disaggregate sample data to mirror known aggregate
distributions of household and person variables of interest;
-
CEMSELTS – Creates additional variables for each individual
and simulates long-term choices; and
-
CEMDAP - Simulates activity schedule and travel
characteristics for each individual of the region.
Documents & Resources
Modeling Task Force Presentation: SCAG Activity-Based Model Development Workshop Presentation
Stage 1 Model Development Reports
SimAGENT Final Report 1 - Overview
SimAGENT Final Report 2 - Opportunity-Based Dynamic Accessibility Indicators in SimAGENT
SimAGENT Final Report 3 - Population Synthesis
SimAGENT Final Report 4 - Activity-Based Travel Demand Analysis
SimAGENT Final Report 5 - TRANSIMS and MATSIM Experiments in SimAGENT
SimAGENT Research Papers
A Joint Vehicle Holdings (Type and Vintage) and Primary Driver Assignment Model with an Application for California
A Methodology to Match Distributions of Both Household and Person Attributes in the Generation of Synthetic Populations
A Household-Level Activity Pattern Generation Model for the SimAGENT System in Southern California
Simulator of Activities, Greenhouse Emissions, Networks, and Travel (SimAGENT) in Southern California
The Application of a Socio-Economic Model System for Activity-Based Modeling: Experience from Southern California
SCAG DTA Model Development & Training

